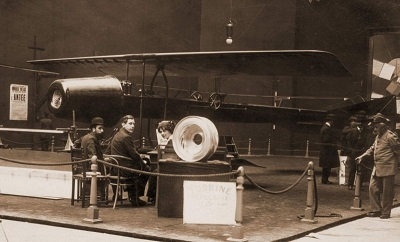
Henri Coanda (7 June 1886 - 25 November 1972) was a Romanian inventor.

Henri Coanda
He was a 24 year old engineer living in France at the time to pursue his dream of making a step further in aviation. The airship was a sesquiplane with cantilevered wings, metal spars and a wooden fuselage, but what was fascinating about it was the novelty of the power-plant.
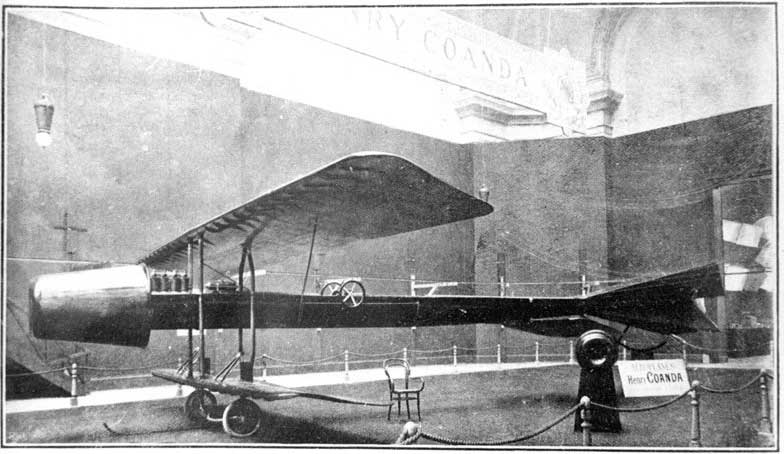
Replica of Coanda's jet - museum in Bucharest
Crew: 1
Type: Sesquiplane
Span: 10.3 m (33 ft 10 in)
Length: 12.5 m (41 ft 0in)
Wing Area: 32.7 sqm
Power-plant: a mixture of jet with piston engine
59 years later he personally explained in an interview that the entire expense for the mysterious aircraft was supported by his family and it was a financial disaster on one hand but a great technicall earning instrument for him.The flight fever was spreading all over the world and inventors were learning flying by experimenting only.It was only 7 years after the Wright brothers and only 4 month after the first self powered flight of Aurel Vlaicu when he patented his own engine called “Propulseur”.
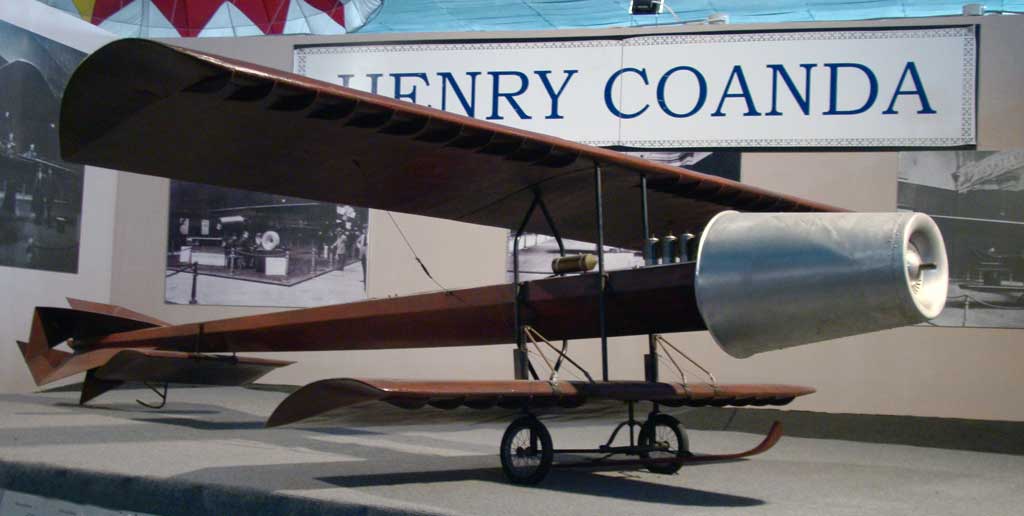

Full-size Replica of the Coandă-1910, built in 2001 ,
National Romanian Military Museum
The principles of operation;
The system consisted of a jet engine with centrifugal blower and post combustion. It used a Clerget internal combustion water-cooled engine, with 4 pistons in line to move the turbine. The pictorial example bellow shows not only the series mechanical arrangement of the components but also the fact that the engine did respect the divergent entry and a convergent divergent topology of a jet. The front on the engine also shows it had no turbine-driven fan and it obtained its thrust as a jet. On the patent granted to Coanda în May 1910 and enhanced în 1911 it was clearly stated that the controlled turbine was arranged to transform the reactions resulting from the flow of the fluid and kinetic energy of the mechanism, in axial reactions to obtain the translation of the vehicle hence its movement.
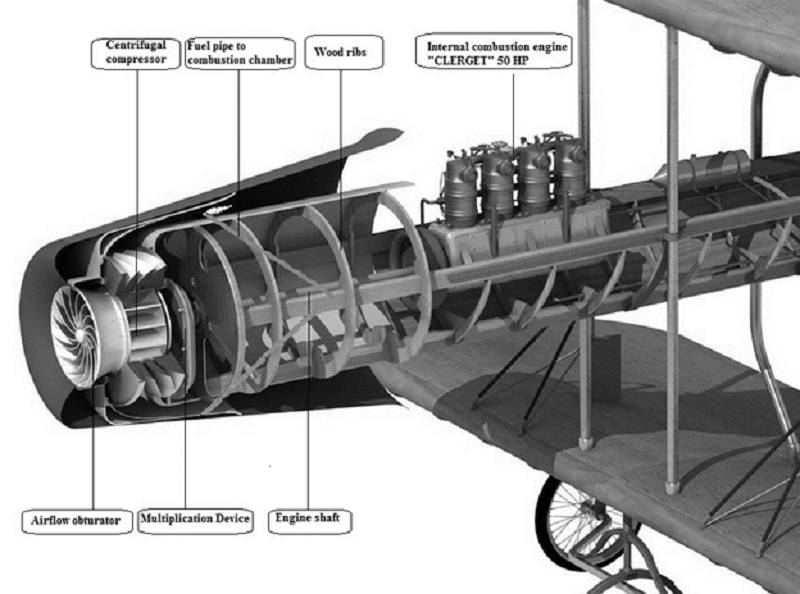
A CAD model of Coanda’s aircraft with notes Enhanced picture from Grabcad.com
Flight trial
On the 10th of December 1910, he tested the airplane himself at Issy -les-Moulineaux, outside Paris and crushed shortly after landing. His intention was to study the aircraft commands during taxi, not to actually fly because he didn’t know how. Due to the high amount of fuel injected in the airstream, the engine started very fast. He tried to lean the mixture and noticed suddenly that he had already taken off and the walls of the city were approaching very fast.Controlling a jet in flight requires different piloting skills that nobody studied at the time.
Legacy
After the crash in 1910, except for paperwork, the project was no longer pursued. The years that followed, aviation increased rapidly and the idea of flying not only with balloons which was already a tradition, but also with vehicles heavier than air, was finally accepted worldwide.
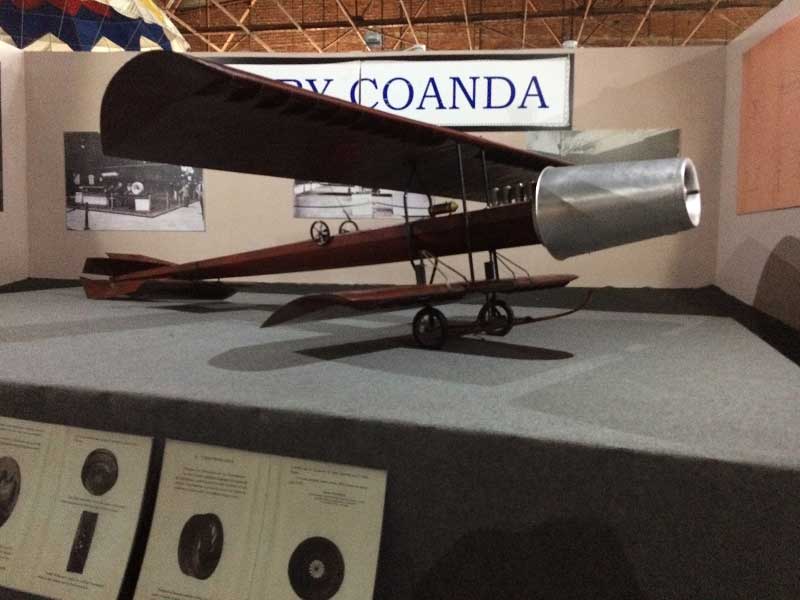

Model of the Coandă-1910 , National Romanian Aviation Museum
Although during WWI the demand for technology and development was high and aviation became a true industry, it was only in 1936, when Hans von Ohain started developing a jet aircraft for the military. They flew for the first time a He 178 model in Germany, on 27 August 1939. In other words, it has been a large gap and a world war full of flying aces and military aviation development until the technology was used. He was truly a man ahead of his time. Some scientists today say that Coanda was born 30 years ahead of his time, actually if you compare the dates it was 29.